How To Search Google Scholar For Systematic Review

Ad Stop using clunky tools and enable your whole review team to collaborate from anywhere.
How to search google scholar for systematic review. Google Search is indeed an imperfect tool to perform systematic reviews. However variable retrieval of content due to regular updating of Google algorithms and the individuals search history and location means that search results are not necessarily reproducible and are therefore not in keeping with replicable search methods required by systematic reviews. For each Scholar search result we try to find a version of the article that you can read.
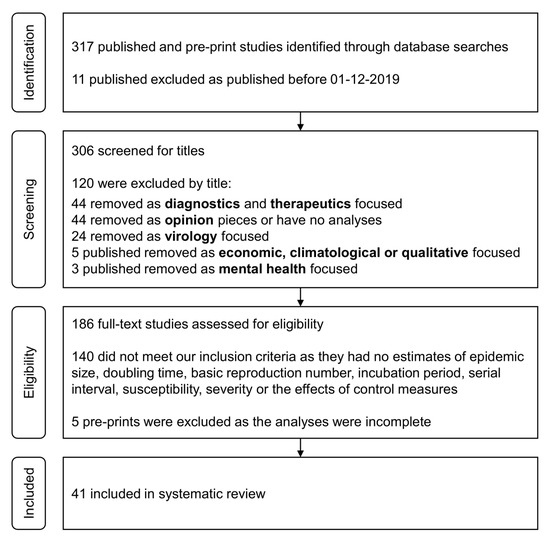
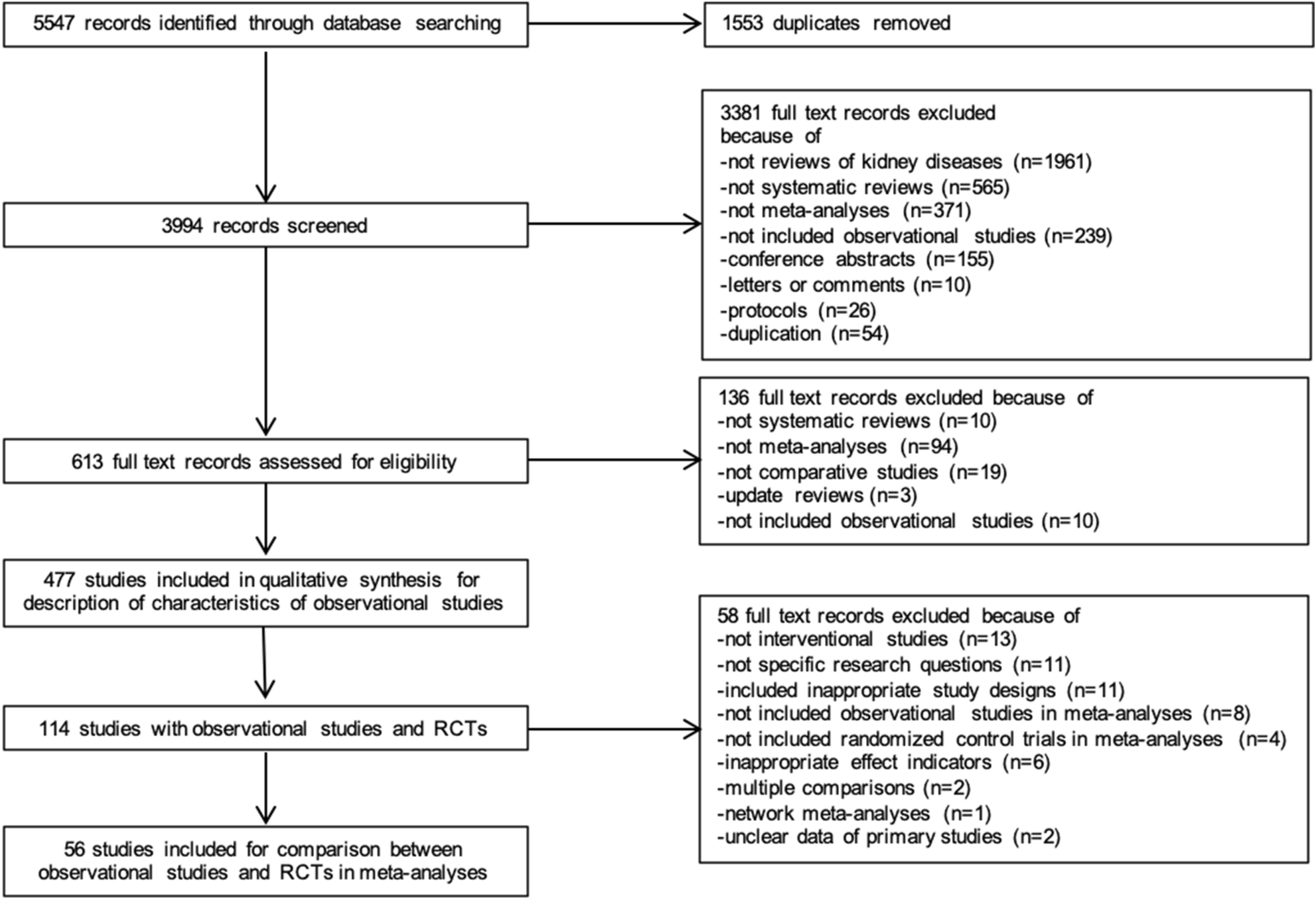
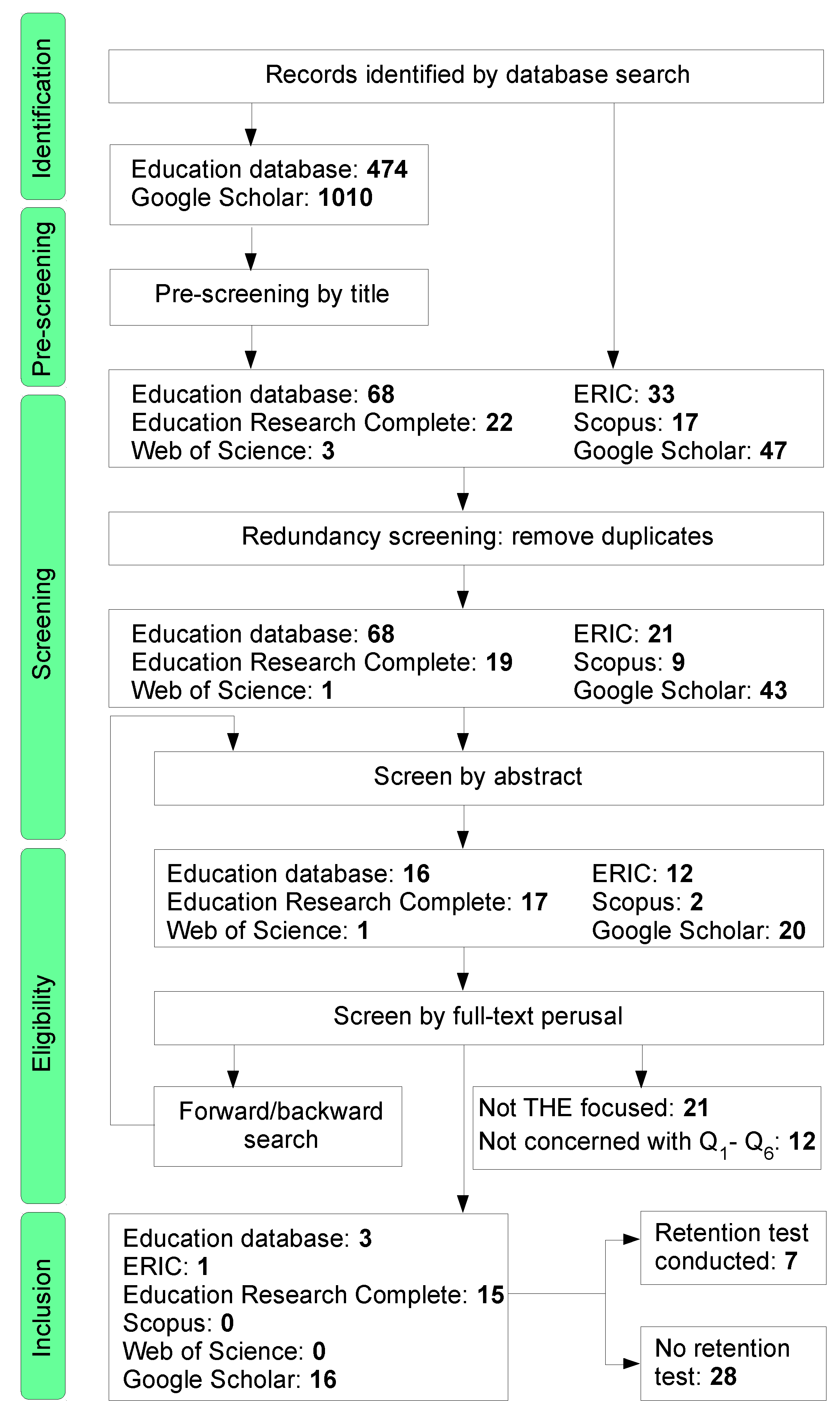
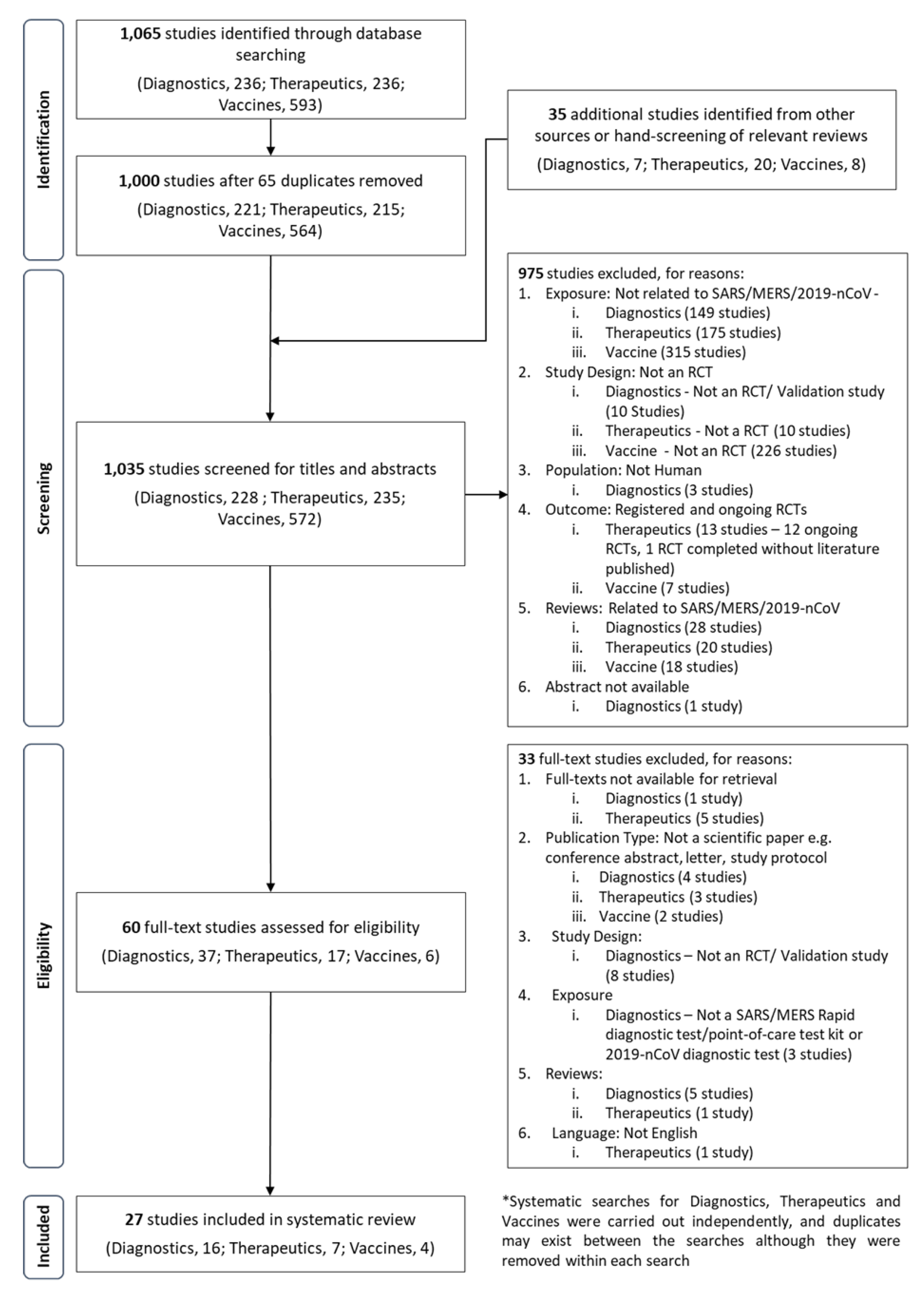
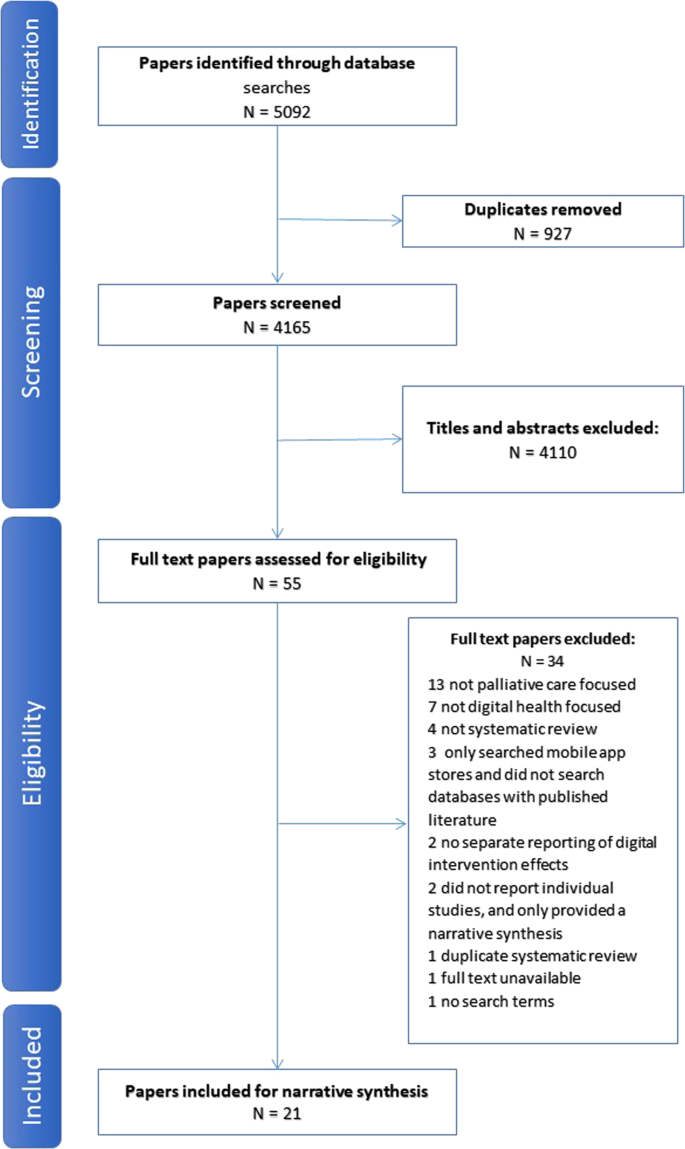
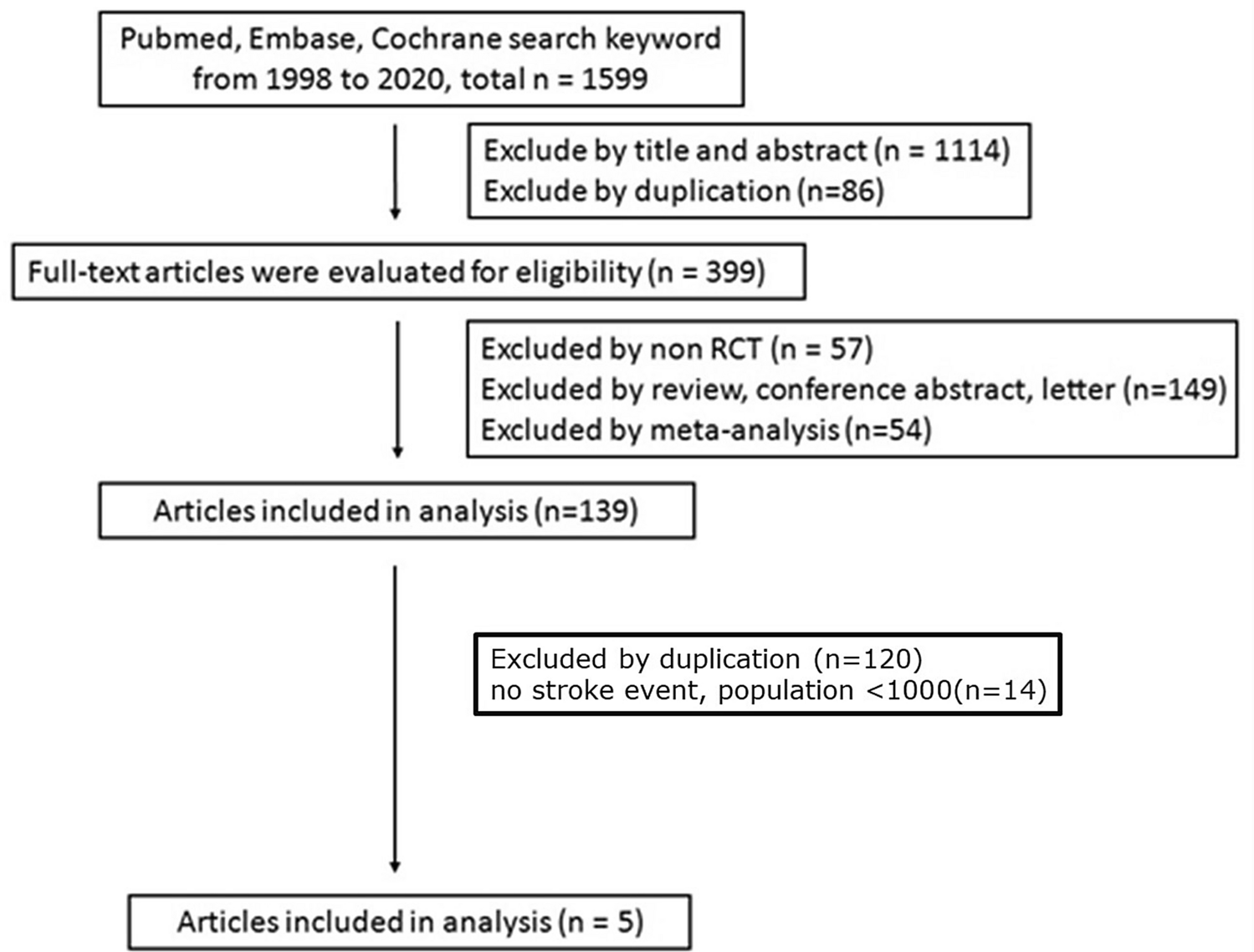
If used in systematic reviews for grey literature we recommend that searches of article titles focus on the first 200 to 300 results. Google Scholar alone has not been shown to retrieve more. We take seriously this concern.
To systematically review research studies that have evaluated the effect of using Google Scholar to identify research studies in health when systematically searching for such studies eg. What approaches can we adopt to support effective systematic searching using Google Scholar. Macros in Microsoft Word have been developed to convert syntaxes between databases and interfaces almost automatically.
To choose for systematic searches is limited and lacking systematic empirical performance assessments. Google Scholar to identify research studies. By combining keywords with Boolean operators and appropriate use of parentheses it is possible to construct search queries of arbitrary complexity.
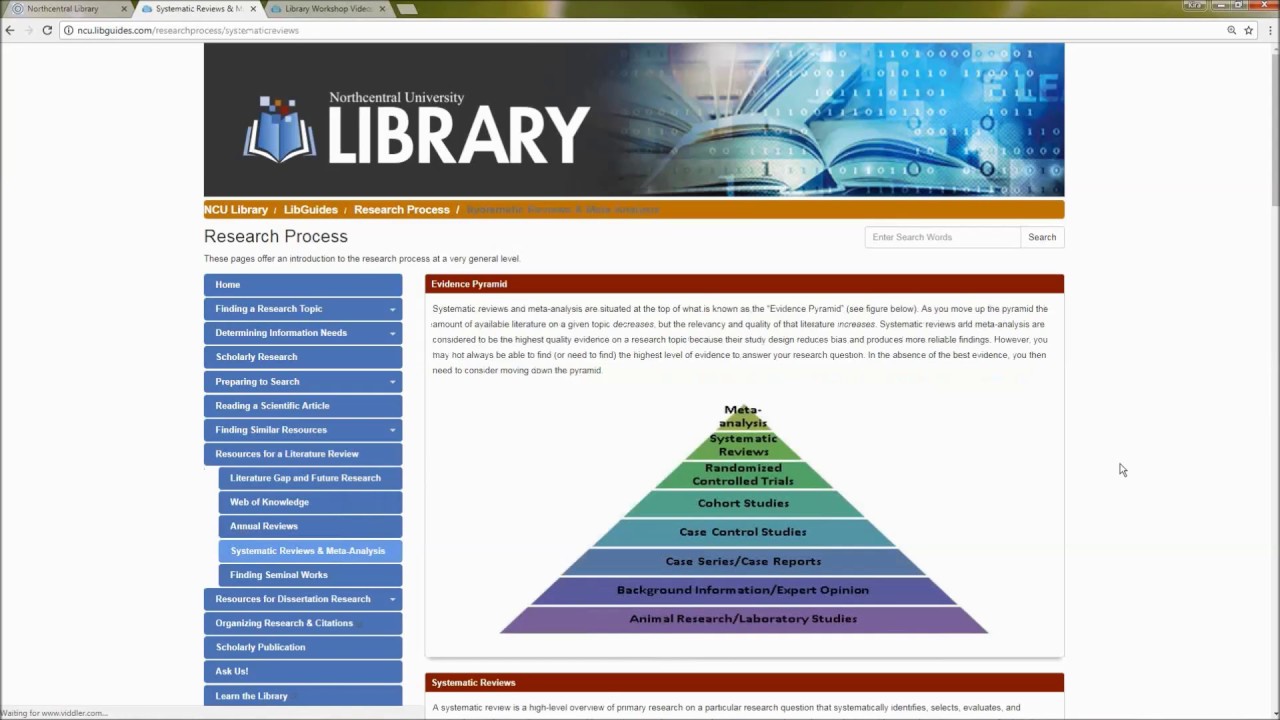
This is a protocol. Click on My library at the top of the Google Scholar homepage or in the left column of a search results page to view all the articles in your library. Optimal searches in systematic reviews should search at least Embase MEDLINE Web of Science and Google Scholar as a minimum requirement to guarantee adequate and efficient coverage.
Is Google Scholar enough to be used for systematic review searching. To be practical therefore most systematic reviewers will create search strategies that are precise enough for them to able to cope with the number of results that are returned but use different methods of searching eg. Contrary to Gehanno et als conclusions that GS could even be used alone 16 we found that GS was not up to the required search standard for systematic reviews.